Build/Deployment Automation
Introduction:-
•
Many of the problems
encountered in software application deployments can be traced to reliance on
manual processes to build, test, and package release targets.
•
Modern software development
practices such as continuous integration (CI) focus on executing integration
builds early and often, rather than waiting until the software product is
almost ready to deliver.
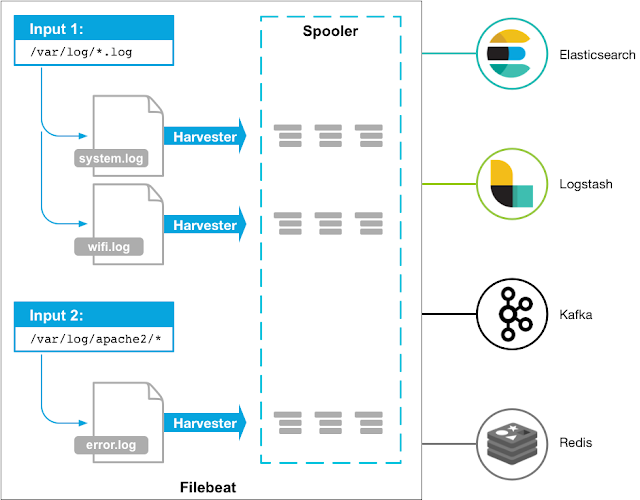
Architecture:-
Benefits Of CI:-
•
Increased productivity
•
Enables shorter feedback cycle
when changes are made
•
Code is kept in a “releasable”
state
•
Code gets back into the hands
of testers quickly
•
Frees the team to do more
interesting and valuable work
•
Improves morale, making it
easier to retain good developers
•
Enables more frequent releases with
new features
•
Improved quality
•
Makes it easier to find and
remove defects because frequent integration and testing identifies bugs as
they are introduced.
•
Multi-platform builds help
in finding problems that may arise on some, but not all, versions of the
supported platform.
•
Reduced Risk
Reduces uncertainty greatly because at all
times the team knows what works, what does not, and what the major issues are
How It Builds:-
- The build is completely automated, usually through the
execution of a single script.
- No matter how triggered or how often run, a build always
begins by retrieving code from the source code repository.
- Unless terminated prematurely, the end product of a build is
always executable code.
- Notification of build status always occurs through a feedback
mechanism.
Continuous Deployment:-
Continuous deployment is “Set of practices and steps that enable us to release working software any time, in any place, with as little effort as possible.”
Continuous deployment is “Set of practices and steps that enable us to release working software any time, in any place, with as little effort as possible.”
•
The build includes compilation,
running all tests and inspections, packaging, and deployment.
•
“Any place” implies not only
developer servers, but also QA and production servers.
Important
Factors:-
•
Code coverage by automated
tests.
•
Security & Load testing to
cope up production environment.
•
Quantifiable measures once
deployed to production.







Comments
Post a Comment